Technology Acceptance Model Wikipedia – The technology acceptance model (TAM) is the theory of information systems that indicates how users are accepted and used.
Using the real system is a point D because people use technology. Behavioral intum is a factor that leads people to the use of technology. Bei’s inttem (BI) is copied by position (A), which is the geral impression of technology.
Technology Acceptance Model Wikipedia

The model indicates that these users are called with a new technology, and a number of factors that fall into their decision on how to use it, in particular: in particular:
Basic Proportionality Theorem (thales Theorem)
External variables, such as social impact, are an important factor in determining the situation. These things (TAM) exist, people will have a position and technology to use technology. However, perception can modify the definition of age and GDER because everyone is different.
TAM 3 has also been suggested in the context of trade E with the inclusion of the effects of trust and risks on the use of the system.
Tam is one of the most ridiculous processes of AJZ and Fishbein in logical work (tra) in the literature. Davis’ technological acceptance model (Davis, 1989; Davis, Baguzi, Warsou, 1989) is the most applied model to accept users and the use of technology (VKATSH, 2000). It was developed by Farid Davis and Richard Baguzi.
TAM replaces many traces of technology acceptance measures – Preparation for use and profit. TA and TAM, which both have a strong behavioral dictation, assume that someone is a job and that it will be free to act without restrictions. In the real world, there will be many restrictions, such as limited freedom of behavior.
Social Media For Outbound Leisure Travel: A Framework Based On Technology Acceptance Model (tam)
Since new technologies such as personal computers are complicated and have found a set of uncertainty in the minds of decision -makers concerning successful accreditation for them, people are positions and positions to try to learn to use new technologies before starting the efforts to use it. Attitudes with regard to use and the time of use cannot be problematic, lack of conviction, or it can only occur after initial technology has evolved to learn to use technology. Thus, real use may not be a direct or immediate result of these situations and situations. [6]
Previous research on publication innovations has also suggested a leading role for ease of use. Tornatzky and Klein
Adoption analysis and have found that compatibility, relative advantage and complexity had the most important relationships with adoption through a wide range of types of innovation. Ison studied the interesting interest in terms of appropriate systems, tasks and functionality profiles, using “appropriate task” terms to describe the scale.

Legris, Engham and Colretete suggest that Tam should be a specific to include variables representing changes and that this can be achieved by adopting the innovation model in TAM.
Artificial Intelligence And Cybersecurity In Healthcare (yel2023)
Lots of attention focused on the sustainability and validity of the questionnaire used by Davis. Adams and others.
To demonstrate the health and reliability of its tools and measurements on a scale. They also stored them to vary the parameters, and using two different samples, they showed the interior reliability and reliability of similar copies of the scales. Hdrickson et al. High reliability and reliability of a good test test.
Szajna noted that Instrumt had predictive healthy use, use and self-declared position towards use.
The total of this research confirmed the health of Davis Instrumt and supported its use with different groups of users and different software options.
Bmw: The Incredible Story Of The German Carmaker
The rehearsal of Davis. They criticized the user scale model and imposed a different model based on three structures: interest, efficiency and ease of use. These results do not seem to have been repeated. However, certain aspects of these results have been tested and supported by the worker
Mark Keel and his colleagues have developed the Davis model (or perhaps more popular) in what they call the network of interest / eou, which is 2 x 2, where each quartet restores a different set of features. In the context of the use of software, this provides a mechanism to discuss the mixture of curt of interest and eou to pack certain programs, and for the plan for a different cycle if the different mixture is necessary, as the more powerful EV program.
The TAM model has been used in most technological and geographic contexts. One of these contexts is health care, which develop quickly

Run the TAM model to integrate the emotion and influence that can play on behavioral ittion to accept technology. More specifically, they looked at a warm deception.
State Of The Art In Li-ion Battery Technology
VKATESH and Davis inhibited the original TAM model to explain the benefit and use perceived in terms of social infection (auto-stands, volunteers, image) and cognitive tools (the importance of the function, the quality of the output, showing a result, the ease of use). The dumped model, called Tam2, was tested in voluntary and compulsory contexts. The results supported Tam2.
Try to integrate the main models of user competition, VKATESH et al. He formulated the uniform theory of admission and the use of technology (UTAUT). This model is observed which exceeds both individual models (modified R-Perct).
In addition, the authors John and others. I also think that the technology acceptance model is ESSTIAL to analyze the factors that affect customer behavior towards online food delivery services. It is also a theoretical model that has been largely adopted to show the acceptance of new technologies. Tam is a series of concepts that explain and predict people’s behavior with their beliefs, attitudes and behavior. In TAM, the ease of use engraved and the perceived benefit, which is supposition beliefs, plays a more dynamic role than sedian beliefs in situations towards the use of a specific technology.
Tam was widely criticized, although it was used by the frequencies, which prompted the original proposals to try to redefine it several times. Tam criticism, as a “theory”, includes skepticism in instructions, clarification and limited prediction, and unpopularity, and the absence of any practical value.
What Is “technology Acceptance Model”? [marketing Model]
Bbasat and Barki suggest that Tam “converted the collision of researchers far from other important research problems and has created an illusion of progress in the accumulation of knowledge. In addition, attempts at the independence of many researchers to extend the TAM in order to adapt it constantly to the variable, the Vinonmts led [which] led to a state of chaos and stability.”
In Gera, Tam focuses on the individual user of a computer, with the concept of “perceived interest”, with exession to bring more and more factors to explain how the user realizes “interest”, and ignores the social processes of Esstille is the Moormt and the arrangement, undoubtedly where technology is really better, social measurement for use. Lanceford argues that the frame of interest perceived and the ease of use ignore other problems, such as the cost and the structural necessities which oblige users to adopt the technology.
The ease of use of perception is less likely to be specific to the situation and the use, according to remote urgent studies, why is technology technology important for intake in the field of technology.

An essential part of the elimination of obstacles that prevent the creation of technology and the adoption of driving technology is to ensure that what has been built not only is complete for various destinations, but also at different levels of understanding and comfort with tools and digital technology.
2024 Mediawiki Conference Highlights
With the continuous integration of digital technology in health and health care systems, through areas such as physical, DSE and remote telephone applications, it is important for developers and technology designers of end user and sympathy for their experience.
Technology can be a tool to improve the quality of services and health results, as well as support staff. However, to have great effects, adoption is the key. For example, a person with limited technological experience and comfort can see certain tools as a waste of time or difficult to use. Consequently, it is unlikely that they successfully adopt technology, even when they provide them with training and education.
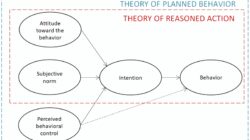
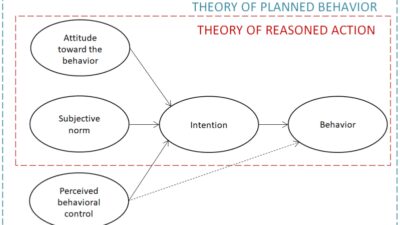
A useful model for understanding how users accept and uses is a technology acceptance model.
This model focuses on two important factors behind the individual’s intention to use the technology: the ease of perceived use and the perceived advantages. As mentioned in the example above, if the user does not see that the technology is reasonable and useful, it will be difficult to reach a successful adoption.
Technology Acceptance Model
Another important factor in this model is that the emphasis placed on the perception of the user and not on the imagination of the technological creator. Although the developer or creator of a specific digital solution may think that the tool is useful and easy to use, if the end user does not share this offer, the tool will have a low probability of accreditation.
Applied applications and health applications are areas in which the technology acceptance model has been considerably studied, in particular in the way in which mobile telephony applications help facilitate relations with patients with service providers. Research extends from studies on the technology acceptance model on service providers and patients for digital applications, and indicates three important areas to consider: access, self-efficiency and perceived incentives.
These areas focus on user experience and feelings all the time