Insurance Cost Japan – The long -term care insurance system was launched in 2000 as a system for the whole society to support the long -term care of the elderly. Municipalities act as insurers, and all citizens over 40 years of age are covered by this system. Compared to other countries, this system is quite generous in terms of coverage and levels of profit. As of April 2016, more than 5 million people were eligible for long -term care insurance. [16]
The foundation of Japan’s long -term care insurance is described in detail in Section 1. Under the elderly welfare system present in the past, municipal governments were finally stated in the selection of services, and since the user could not choose services, the contents of the services were uniform. In addition, since the service fee was based on the ability of a patient to pay, people with moderate and high-level income should be heavy burden, and general hospitals began to face problems related to long-term hospitalization for long-term care.
Insurance Cost Japan

With the rapid aging of the population, the number of people requiring long-term care as well as the length of care also increased, and long-term care requirements increased. At the same time, the status quo in which families traditionally began to meet the needs of the elderly, change towards nuclear families and with the aging of that generation that provided care. [1]]
High-cost Medical Expense Benefit|traffic Accident Interpretation Japan
After taking into account such issues and changes, Japan developed a kind of care insurance system in a way to support the long -term care of the elderly for the society.
Induction Independence Support: To go beyond providing only long -term care and also support the freedom of elderly people.
As user-oriented system: providing users integrated access to health and welfare services from diverse institutions at their own discretion.
These Social Insurance System: Planning a social insurance scheme with a clear relationship between profit and burden.
Japan Health Policy Now
In long-term care insurance, Enroll is divided into two categories-of which age 65 and above (category 1 insured) and are aged 45 to 64 years, concurrently nominated in other medical insurance schemes (category 2 insured).
And category 1 insured: eligible for services, whether they obtain certification for long -term care needs or certification for support requirement.
And category 2 insured: Eligible for services are only eligible for services only after receiving certification for long -term care requirement or certification for the need for support due to diseases related to aging (specified diseases).
At the end of FY2015, 33.82 million people were counted in category 1, and 42.04 million people (as per the monthly average published in 2017, 2017).
Japan Living Costs: What Indian Students Should Expect
Category 1 Annrolis (age 65 and above) pay your health insurance and long -term care insurance premium separately. Premium and insurance rates are determined by the municipalities and are judged at nine standardized levels of income. [20] For category 2 Enrolls (age 40 to 64), health insurance and long -term care insurance premiums are paid simultaneously in lump sum. [21]
Around the installation of long -term care insurance systems, there was a great deal of debate on the justification behind targeting people over 40 years of age. Between various opinions, people over the age of 20 were supported to target, but it was indicated during the consultation on the long-term care insurance system in the council for health and welfare in 1996 that once people go through the age of 40, there is a possibility that they would have to take care of their parents and thus need to increase social support. As a result, it was decided to enroll people over 40 years of age and since long -term care costs should be supported by society as a whole. It was through such discussions that the current system took shape. (MHLW, 2006)
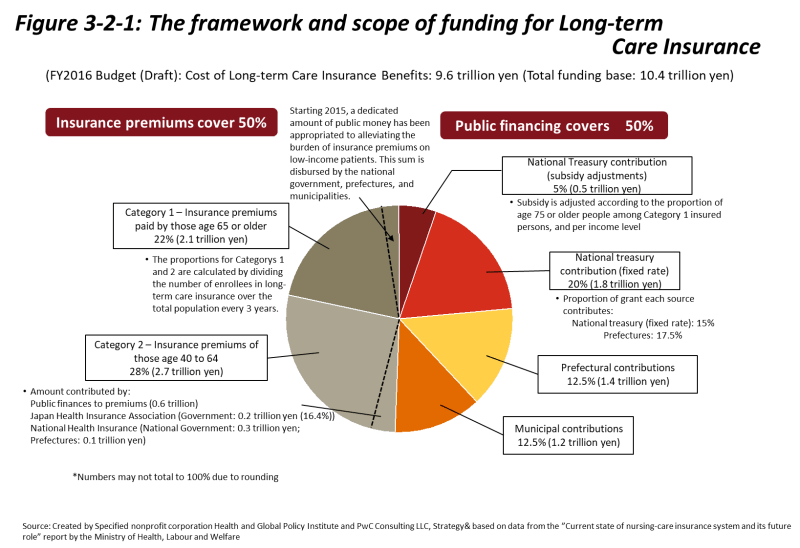
As shown in Figure 3–2–1, half-term care comes from the Enerolli premium for long-term care insurance, while the other half comes from public funding. The budget for long-term care benefits was determined on 9.6 trillion yen in FY2016. Funds were sourced from Category 1 Premium (2.1 trillion yen), category 2 premium (2.7 trillion yen), National Treasury (2.2 trillion yen), province (1.4 trillion yen), and municipalities (1.2 trillion yen).
Similar to medical expenses, long-term care expenses are increasing annually along with increase in profit costs, and this trend is expected to continue in the future due to aging of society in Japan. [22]
How To Get Property Insurance In Japan For Foreigners
Funding and financial burden imbalances exist among the provinces as a result of the fact that the provinces with high ratio of people above 75 years of age, increasing profit pay-outs, and provinces with low average income levels face falling revenue. Financial action is being taken, five percent of the 26% stake provided by the National Treasury are subject to fiscal adjustment. The system of adjustment tolerates close similarity for the initiative within the medical care system for the elderly (explained in Section 1.2) in the sense that both systems are designed to help reduce the imbalance between fiscal resources of various insurers.
To use long -term care services, applications are submitted to municipal government offices or comprehensive community support centers. To achieve qualification, applicants must obtain a certification of long -term care requirement or certification of necessary support. When the certification is obtained, the care managers prepare a plan for the applicants, making them capable of using various services.
A person’s required care level (classified as preventive aid level 1 or 2, or long-term care levels 1) is determined by a committee of experts who takes into account written diagnosis and an on-site survey from a attending physician that addresses 74 items related to the activities of the person’s daily life. The suitability of the person’s care levels is then re -evaluated every two years or after a decline marked in health. [23] The number of people requiring care is shown in the annual trend Figure 3-2-2.

To address the fact that there is no decrease in demand for long -term care and a mild degree of care is required to curb a continuous increase in population (preventive support level 1 / long -term care level 1), the 2006 revision of the Long -term Care Insurance Act introduced preventive care services. At that point, the first certified recipients were divided into long -term care levels 1 or preventive support level 2 to achieve care level 1, depending on whether their condition was likely to improve or remain the same.
Insurance Card Nabanayani Hunxa In Japanese Language
Prior to the installation of the long -term care insurance system, the care of the elderly was divided between a system of welfare for the elderly and a system of healthcare for the elderly. To ensure that people who were receiving welfare services could continue to use similar services in the new system, certification criteria were relaxed. This caused immediate increase in the number of users requiring in-hom care or light care (preventive support level 1 / long-term care level 1), thus speculation in intensive care nursing homes and made long-waiting lists. (Ekgami Naoki, 2017)
,
,
,
Solved: The Cost Of Refined Oil When Shipped Via The Malacca Straits To Japan In Dollars Per Kilol [math]
,
,
] In recent years, due to the depreciation of the yen, attractive real estate market and long -term investment opportunities.
Japan has no restrictions for their own assets on non-Japanese citizens, and requirements and procedures for their own property are generally the same for Japanese citizens.
Dental Cost(tooth Filling) In Japan Without Insurance🇯🇵
However, being the owner of a property is not just about buying it; It also includes responsibilities like insurance, tax and management.
This article will suggest to choose the types of property insurance in Japan, non -resident house insurance, insurance cover type and correct insurance and reduce costs.
Japan has a complex insurance system, and choosing the right plan can be challenging. The type of insurance and insurance premium depends on personal needs.
It can be very difficult to understand the conditions of local laws and regulations and insurance policies written in Japanese. Language barrier often prevents foreign property owners from choosing optimal insurance schemes, leading to important problems.
Health Check: The Cost Of Medical Care In Japan
A customer shared his experience in an attempt to get the insurance of the owners of the house as an non -resident: “I originally tried to go through a local agent in Japan, but they needed a Japanese phone number, which I could not find without residence.”
For non -resident property owners, information can be challenging to receive an insurance bill and sent to their Japanese property. Note: Many non -resident property owners use, a virtual mailbox service that uploads all the upcoming mail to a cloud account. Service also provides a bill payment
Pet insurance japan, japan medical insurance, travel insurance japan cost, japan travel insurance, japan trip cost, japan insurance companies, japan health insurance cost, health insurance japan, insurance japan, japan travel cost, life insurance japan, car insurance japan