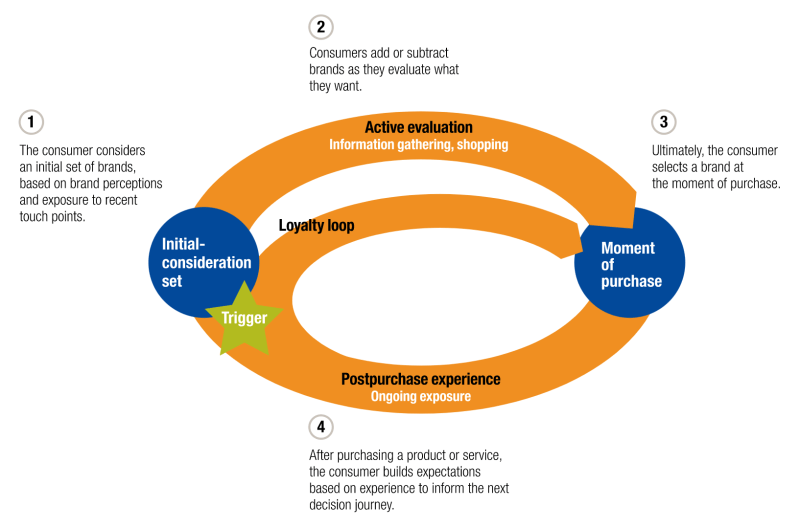
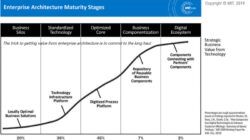
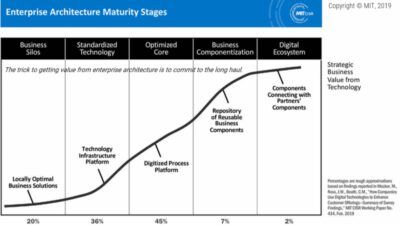
Technology Acceptance Model Example – Technical Adoption Model: Is it used/costly for technical rates, psychological trends or pedagogical reasoning in the context that is taught during the Covid-19 pandemic period?
The impact of the education on Covid-19 was shaken both practical and researchers. Practitioners used the technology immediately, which placed the shock to the individual. Destruction of people’s response to why technology is accepted or acceptable and not used/used has a significant impact on education. This concept paper presents the process used to develop theoretical foundation based on the accepted tecnolology model. Originally, the configuration of the Tam and Extended Tam explored so that the “why” practice teachers can choose the technology for education purposes at elementary and secondary school levels during the Pandemic Covid-19 period. Tam was criticized for being simple and narrow. Many researchers criticize Tam’s because they cannot confirm their discovery or because the structure does not fit its demands. This paper challenges this critical. The theoretical foundation proposed in this paper represents a view of the reality of relationships in relation to the influence of variables that potentially relax or control emotional and mental reactions. It contributes to the existing literature in a comprehensive review of the concept, composition and Covid-19 “event” situation. The results are given as follows: contextual reality and application often require theoretical foundation based on complex questions and answers. Proposed effects in the single direction of the recognized use of the useful recognition (PU) can be challenged at theoretical base cast. To ignore what is not used as a fact is a study focused on testing theory seriously interfering with the possibility of applying tams, and the TAM provides sufficient flexibility when the door is open for adaptation, which is the advantage of social science research.
Technology Acceptance Model Example

The research agenda is generally known in examples such as current events and difficulties (Covid-19), political and rescue orders (decomposing, rural education approach), and education demands (enhancing learning and education; 21st century.). In the education context, the focus study of technology adoption recently raised in a somewhat forced situation due to the recent Covid-19 pandemic (2020 …). The use of educational technology for education and learning does not spread in all social and education contexts. The ERA Pandemic Covid-19 challenges the relationship between teaching and education technology during the Covid-19 period. In this regard, the Government and the Cobid -19 policy forces many educational practices to provide transformation into urgent online remote education and hybrid methodology. This basically suggests the use of technology for education and learning. In addition, during this period, the relationship between technology and education suggests a sharp change in practice, and in many cases it may not be a practical knowledge of teachers, especially teachers in elementary and secondary schools.
Factors Influencing Continuance Intention To Use Mobile Banking: An Extended Expectation-confirmation Model With Moderating Role Of Trust
The development of technology and demands and demands can be located as “events” on time. Many before “events” in history have changed many the world with people. For example: Bubonic outbreak (14th century); Spanish flu (1918-1920); Other events including the Asian bird flu (H5N1: 1959-1991) and mechanization of the industrial revolution (mid -18th century); World War II; Silicon Revolution (after 1947); Covid-19, such as the development of the age of electricity, the sea, air, roads, and railroad trips, has become one of these “events”, which adopts the concept of “events” and represents the Covid-19 context. Forced rules for educational context, the meaning of the Covid-19 event suggests that there will be a change in the behavior of technology adoption and use. Some of these changes may be taken instant with time, but some are permanent and some cases temporarily. As a result, behavioral changes are based on personal basic survival choices and sophisticated demands for self and learners.
The study of technology adoption has been informed in many cases by the TAM and its derivatives since the late 1800s. It has been used in various fields such as education, information systems, agriculture, health, and financial services, and investigates aspects such as mood in technology use, use of technologies for specific topics, mobile use of technology and social networks. Use services. Some studies are as follows:
• Davis (1993) was accepted at work. Fariza et al. (2021): In kindergarten math class and elementary school, we evaluate the teacher’s look at learning technology.
• Jarvenpaa and Staples (2000) and Dasgupta et al. (2002) Adjust TAM for technology adoption in Internet 2.0 environment. Sánchez-Franco (2009) enhances the Tam model with the effect of the emotional recognized quality; Hossain and De Silva (2009) expand its TAM into consideration social links to understand social networking systems. Cheung and Vogel (2013) extend Tam’s to explain factors affecting the acceptance of applications for collaborative learning. Pituch and Lee (2006) added the system and features learners as an external variable in TAM. Diop et al. (2019) Expand TAM to understand the adoption of traveler variable messages.
Enablers And Disablers For Contactless Payment Acceptance Among Malaysian Adults
• Gong et al. (2004) and Sánchez-Franco (2009) developed the theoretical model to understand the behavior of student learning technology. Lee et al. (2005) is an integrated Tam with motivational theory; Liu et al. (2005) Understand Learning Systems using TAM and flow theory.
• Sayel and Rahman (2003); Porter and Donthu (2006), Li and Kirkup (2007) and Edmunds et al. (2012) Explore the use of the Internet at University. Sánchez and Hueros (2010) saw acceptance of Moodle. Fathema et al. (2015) expand its TAM to investigate the use of the LMS faculty in higher education institutions.
• TSAI (2015): TAM has been applied to explore the effects of CMS writing education. Ajibade (2018) explores the boundaries of TAM in current application and the use of science -related technologies. Wannapiroon et al. (2021) explore online education technology for professional instructors in a new normal education.

From the beginning, Tam was praised and criticized. Many critical points that Tam’s is too simple and takes a narrow view that focuses solely on the beliefs, awareness and intention of individual inhabitants. This paper is not a critic of the Tam, but a deeper exploration of implied adoption decisions that may explain fundamental decisions and actions in different situations depending on the situation.
What Is A Digital Strategy And How Should It Be Structured?
As a theoretical desktop study using two -dimensions, this paper uses the infrastructure to understand individual behavior related to TAM’s extensive perspective, theory that supports TAM, follow -up repetition in Tam, technology/non -adoption acceptable and used. Not used. The focus of the paper is “why” questions. According to Sadeck (2016, P. 222), “Why” is a complex question. Complex questions provide complex answers. Bagozzi (2007, p. 244) said, “…” The mechanism or “reason” behind the proposed interaction effect is rarely given. ”The reason for this paper is to release complex answers without academic discourse in a way Simple to understand a simple way to understand the complexity of technology/non -adoption in the education context.
In the context of this paper (available in elementary and high school), it is considered revenge and is considered to be the following.
• Systems and services such as social networking services (SNS); Video conferencing facilities; Learning Management System (LMS); Back
Two focus of extensive studies (see Figure 1) show that the theoretical test (in the context of the study confirms or rejects the applicability of the basic configuration of the basic configuration) or the theoretical output (adoption of technical adoption) to understand “as A reference foundation. Mutual: Technical contracts; psychological trends and educational reasoning form a focused lens.
The Effect Of Digital Literacy On Technology Acceptance: An Evaluation On Administrative Staff In Higher Education
Historical: Technology Adoption Model and Development: TAM- TAM 2- TAM 3-UNIFIED Technology acceptance and use theory
This section will briefly present this synthesis: reasonable behavior theory (Tra; Fishbein and Ajzen, 1975); Planned Behavior Theory (TPB; Ajzen, 1985, 1991); Models accept original technology and extension (Tam; Davis, 1986; Davis et al., 1989), Technology Acceptance Model 2 (TAM2; Venkatesh and Davis, 2000); Unified theory of accepting technology and use (Utaut; Venkatesh et al., 2003) and technology accepted Model 3 (TAM3; Venkatesh and Bala, 2008).
Fred Davis, which invented an original technology acceptance model (TAM: developed 1985 -Publish 1986, Figure 2), mentioned the following two goals: First, you need to improve your understanding of the user acceptance process and provide a new theoretical insight into The successful design and application of information. System. Second, TAM must provide a theoretical basis for “user acceptance test” methodology (Davis, 1986, p. 7). Meerza (2017, p. 52471), which matches these goals, said, “to determine the possibility of a final user who adopts a specific technology. Understand internal and external factors that affect certain user groups that adopt or provide certain technologies.

According to the analysis, the two specific beliefs, meaning useful recognition (PU) and recognized convenience (inexpensive), are found to be the pole crystals in the Tam and the repetition afterwards. Logical present