Technology Acceptance Model Formula – This item is a part of the study for timing in Covid-19 times: Students, families, families’ perspectives 41 Articles of Articles
Research: Ani Covid-19 and the resulting situation forced the university and didactic approach by changing teaching cases for completely virtual and online learning methods. Today, “forced” distance education and learning status has been created. This study aims to aim the impact of these innovations on the implementation, acceptance, acceptance and use of the virtual teacher proposal within the framework of the acceptance model (full).
Technology Acceptance Model Formula
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/diffusion-of-innovations-theory.asp-final-7ffecfaf70054216b54d7d5fe1d17e32.png?strip=all)
Methods: A total of 218 students and a German Faculty of Medicine Pulse 69 leakage, acceptance, satisfaction and (FDT) (FDT) (FDT) (FDT) completed online surveys. A expanded version of Tam was used to evaluate students’ acceptance and storticals of students and FDL and FDT. In order to estimate multiple variable addictions, the road was analyzed with structural comparative models (SEM).
Theory Of Reasoned Action
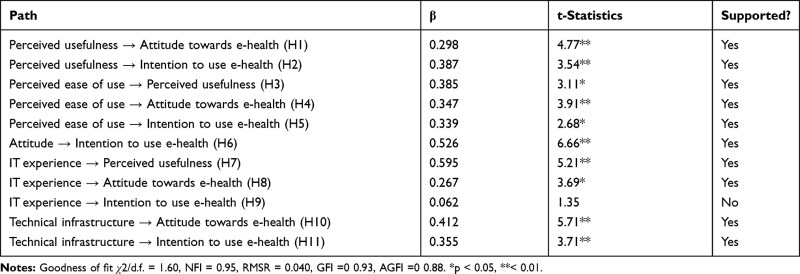
Results: In general, students reported and teachers and lectures are satisfied with the implementation of FDL and FDT. Regarding the full model, the adaptation index proposed an acceptable model for both groups. The model of the students revealed that perceived utility is a powerful predictive power in the perceived convenience to predict the attitude and attitude towards use. The current technical infrastructure, such as general concerns about the media, is positively related to the organization of observed useful and online learning. The useful positive power perceived in use was also evident for teachers in the model, and technical infrastructure envisaged use observers in teachers.
Conclusion: Exactly, it is a suitable framework for representing the implementation, acceptance, acceptance and use of the virtual sloping song during the special pandemic situation at the university. However, personal and structural context factors are important determinants for observed usefulness and ease of use observed in the student group. It makes it difficult to predict the real use of virtual learning based on attitude, which is forced to teach and forced to teach.
The rise of the Internet and the development of modern technologies affect education and learning. Nevertheless, while traditional doctrine and learning take place in physical classes, online learning is exception despite the limits of size, place and time in most universities (Liu et al., 2010). Due to the sudden eruption of the disease-Covid-19 disease, German universities would prepare an online / digital period since they were not allowed face-to-face [Hoch), 2020]. This would be done under pressure when events had to take action quickly. The situation challenged the education systems in German universities and forced all participating people to move into leather learning mode. Students and teachers in RWTH Aachen Universe had to prepare for a digital period in a very short time. University Hospitals Medical Faculties Pandemik took part in a special role. In this study, the difficulties of introducing the introduction of the digital lighter since sin since the medical care of medical care, pandemi. Moreover, theoretical content medicine included numerous practical courses, practical skills, practical skills, and the doctrine of laboratory studies that are difficult to learn or learn. Because of these challenges, we are interested in the acceptance and satisfaction of RWTHEUREN from RWTHEUREN. Since students and teaching had to be prepared for a digital period due to restrictions on COVID, we called this issue as “forced distribution and learning” (FDT; FDL).
In this study, the proposed model based on the model (fully) accepted as a framework for understanding the role of acceptance and satisfaction by virtual learning method in the case of FDL and FDT. Exactly, internal beliefs (useful use) deals with the theory of action by Ajzen and Fishbein (1980) to explain the causal relationship between the attitude of users (Davis, 1989). More recently, it has made it a solid model to estimate its acceptance when it comes to technology (Venkatesh and Venkatesesh, 2000; Legis et al., 2003)., 2003)., 2003)., 2003)., 2003). In addition, it attracted full attention in e-learning research (Auja and Thatcher, 2005; Sumak et al., 2011; Shin and Kang, 2015). In its original form, a model takes its behavior with a voluntary attitude to use a technology (ATU) that provides a behavioral savings. In general, instead of focusing on technology itself, it is necessary to measure attitudes and beliefs related to technology and can keep the individual unfavorable. Attitudes consist of a person’s beliefs that may affect each other in the use of a particular technology. The first belief is the idea of ”perceived cousin” (PU-PU), which expresses the “subjective opportunities of the use of a particular apprentice system” (Davis, 1989, p.320). The second belief “Observed Use” (Peou) “Note that the user expects the target system to be free from efforts” (Davis, 1989, p.320). The model is also the effect of external variables such as draft properties that may affect cognitive factors. These variables, which attract attention in the research, can understand how cognitive factors or how PU and PEOU can be manipulated (Can and Gopal, 1995). At a very early stage, Venkatesh and Davis Illustrated (1996) can be increased by such expansions. Yousafzi et al. (2007), in addition to other variables, they classified several external variables in the four organizational, system and personal characteristics categories of users. Other studies prefer to be handled in a pair and specific factors, eg. Personal factors or playful factors (Ay and Kim, 2001; Estregana et al., 2019) or learning styles (Al-Azawei et al., 2017). Rawess et al. (2014) was found to be a safe factor for the full model. Trust is about the security of information placed on social media sites. For our goals, we have described a similar structure that we talk about the protectors who worry about the abuse of data and worrying about video conference programs. Another interest in our study was the construction of technical support or investigated by various researchers (Baba’s Research et al., 2015 Servidio and Cronin, 2018). The examination of Servidio and Cronin (2018) found that technical support, defined as interventions by technical personnel to help students use, affects the usefulness and convenience of use. For example, we defined our technical infrastructure (TI) structure for good internet quality or appropriate equipment aspects. Other studies (Persico et al., 2014; Baba (2015), the importance of the system components in addition to the existence of technical infrastructure, that is, the organizational aspects related to the organizational aspects related to the students in our study, is also talked about personal variables such as the user (2015), and the personal variables such as the user (2015).
Making The Fogg Behavior Model Actionable
The main purpose of the study is to define and learn a theory -based, expanded full model. The focus was to see if the pandemic conditions had an effect on the acceptance and perceived usefulness of the virtual skin. The hypothesis in which some personal and structural factors were more important in this forced COVİD-19 session than cases without pandemic conditions, for example, was not the inability to buy some technical equipment. In our study, we ask a expanded full model with external variables that may affect the acceptance and use of the virtual.