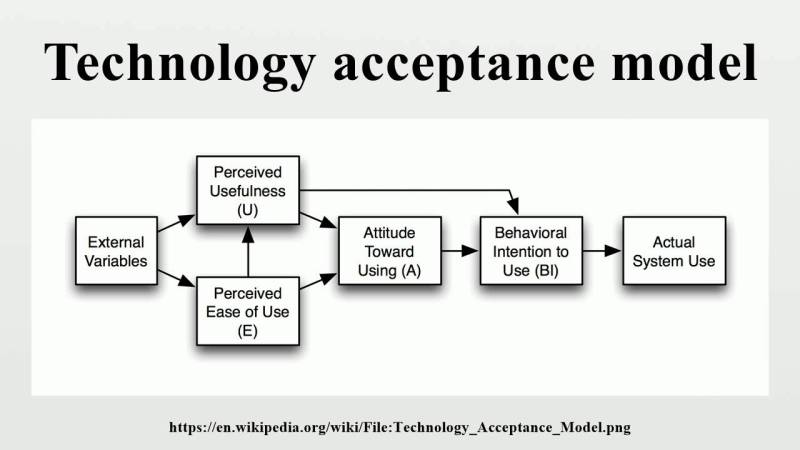
Technology Acceptance Model Fred Davis – The Technological Acceptance Model (TAM) is a theoretical framework developed to explain how users adopt and use the technology. It is a widely used model applied in various fields, including information, marketing and social science systems. Tam was first suggested by Fred Davis in 1986 and has since changed and expanded by many researchers.
TAM is made up of two main ingredients: the detected utility (PU) and the ease of detected use (peou). PU refers to the level at which a user believes that technology will improve their performance or productivity. Peaou refers to the level at which a user believes that a technology is easy to use. According to Tam, these two factors are the main determinant of acceptance and behavior of users.
Technology Acceptance Model Fred Davis

Although PU and Peout are the main factors of TAM, external factors can also influence the acceptance and use of users’ behavior. These factors include social standards, organizational factors and differences of individuals. Social standards refer to others’ expectations and beliefs on the user’s social network. Organizational factors refer to the policies, methods and cultures of the user organization. Individual differences refer to factors such as age, gender and experience.
Information Technology Adoption In Indonesia’s Small-scale Dairy Farms
TAM is widely used in various fields to study the adoption and use of users’ behavior. It is applied to the context of E -Commerce, mobile technology, social networks
, and health technology, among others. TAM was also used to develop and evaluate interventions aimed at increasing the adoption and use of users’ behavior.
Despite its widespread use, TAM is criticized for limited reach and predictable power. Some researchers argue that TAM does not consider factors such as social influence, confidence and risk realizing. Others argue that TAM has not properly acquired the complex properties of users’ behavior.
To meet some of Tam criticism, many researchers have suggested extensions and modifications in the model. For example, the one theory of receiving and using technology (UTAUT) includes additional factors such as performance, expectation of effort, social influence and facilitating conditions. Other researchers have suggested changes to TAM to consider specific contexts or groups of users.
Technology Acceptance Model
The technological reception model is a widely used theoretical framework applied in various fields to study the adoption of adoption and use of users. While Tam has limitations, it provides a variety of starting point for understanding how users have adopted and uses the technology. In incorporating external factors and considerations of extensions and modifications in the model, researchers can continue to perfect our understanding of users’ behavior and improving the design and implementation of the technology.
Understanding the use of users in technology adopting is important to any business or organization that wants to successfully implement new technologies. The Technological Acceptance Model (TAM) is a popular framework that helps companies understand the use of users and to predict their acceptance of new technologies. In this section, we will see different aspects of users’ behavior and how it relates to technology adoption.
1. Perceived Utility: One of the main factors that determines users’ behavior towards technology adoption is noticed utility. Users are more likely to adopt technology if they believe they can help them achieve their goals or facilitate their work. For example, if a new software program promises to justify the process of accounting a business and make it better, employees are more likely to adopt it. On the other hand, if the benefits of software are not conveyed or clearly understood, users may be more likely to adopt it.

2. The ease of noticed use: Another important factor that affects users’ behavior is the ease of noticeable use. Users are more likely to adopt a technology if they think it’s easy to use and browse. For example, if a new mobile application is easy to understand and easy to use, users are more likely to continue using it. However, if the application is difficult to browse or require a lot of effort to use, users may be more likely to adopt it.
Pdf) A Technology Acceptance Model For Empirically Testing New End-user Information Systems: Theory And Results
3. Social Influence: Social influence is another factor that affects users’ behavior in technology adopting. Users are more likely to adopt a technology if they see others use it and if it is accepted in society. For example, if a new social media platform is gaining popularity and widely used by friends, users are more likely to adopt it. On the other hand, if one technology is not widely accepted or used by others, users may be more likely to adopt it.
5. Trust: Trust is another important factor that affects users’ behavior in technology adopting. Users are more likely to adopt a technology if they trust the supplier or technology themselves. For example, if a company has a good reputation to provide reliable and safe technology, users are more likely to adopt new technologies from this service provider. On the other hand, if a company has a bad reputation of security or reliability, users may be more likely to adopt new provider’s new technologies.
5. Training and Support: Finally, training and support can also affect users’ behavior in technology adopting. Users are more likely to adopt technology if they receive proper training and support to use it effectively. For example, if a company provides comprehensive training and support for a new software program, users are more likely to adopt and use it effectively. However, if users do not accept proper training or support, they can be combated to use the technology effectively and may be more likely to adopt it.
Understanding the use of users in technology adopting is important for companies and organizations who want to successfully implement new technologies. In consideration of factors such as the utility, the ease of noticeable use, social influence, confidence and training and support, companies can predict users’ behavior and adapt their technology -adoption techniques accordingly. Eventually companies prioritize users’ behavior
Demystification Of Readiness, Security, And Technological Enhancements In The Adoption Of A Cashless Economy
The noticeable utility and the noticeable ease of use are two important factors that influence the reception of users’ technology. These factors are part of the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM), which is a theoretical framework that explains how users have adopted and uses technology. The detected utility refers to the level at which a user believes that technology will improve their performance, while ease of noticeable use determines the level at which a user believes that a technology is easy to use. In this section, we explore these two factors in more detail and discuss their importance in the process of receiving technology.
The detected utility is a critical factor in determining whether users will accept a technology or not. If a user sees that a technology is useful, it is more likely to adopt it. For example, if a user plans to buy a new smartphone, he or she will weigh the benefits of the new device with update costs. If you believe the new device will significantly improve your productivity or recreation experience, you are more likely to buy.
The noticeable ease of use is another important factor in receiving technology. If a user sees it is easy to use a technology, it is more likely to adopt it. For example, if a user plans to move from a traditional computer to a tablet device, they will weigh the benefits of the new device with ease of use. If they believe that the tablet is easier to use and more convenient than a traditional computer, it is more likely to change.

Both noticed that utility and the ease of use received are important factors in receiving technology. If a technology is seen as useful but difficult to use, users can still use if they believe the benefits exceed costs. Similarly, if a technology is seen as easy to use, but not very useful, users are more likely to adopt it. Therefore, technology designers should strive to create a useful and easy -to -use products.
10 Things To Know About The Technology Acceptance Model
An example of technology that is very useful and useful use is the iPhone. The iPhone is seen as useful because it allows users to perform a variety of activities such as internet -surfing, sending emails and taking photos. It is also considered easy to use for its intuitive interface and its simple design.
On the other hand, a technology with little use and ease of use is Google Glass. Google Glass is a device that can be carried that allows users to access information and perform tasks through voice orders and a small screen. However, it is difficult to use by many users and the benefits of the device are unclear, leading to low adoption rates.
When designing technology, designers should consider the detected utility and the ease of noticeable use. One option is to focus on creating a very useful -useful technology, but it can be more difficult to use. This method may be suitable for technologies that
Thoughts are an important factor that plays an important role in receiving technology. Thoughts are defined as a positive or negative evaluation of something, such as technology. Thoughts are made up of a variety of factors, such as beliefs, emotions and past experiences.