Technology Acceptance Model Graph – The technology acceptance model (TAM) is the theory of information systems that model how users accept and use technology.
The actual use of the system is a D-point where people use technology. The intention of behavior is a factor that means people use technology. Intention in behavior (Bi) is blown towards attitude (a) which is a geral impression of technology.
Technology Acceptance Model Graph

The model suggests that users are achieved by new technology, a larger number of factors that will use their decision on how the WH will use, especially: especially: especially: especially: especially: especially: especially:
Exploit The Product Life Cycle
External variables such as social inflammation is an important factor for determining the attitude. Although these things (darkness) are present, people will have an attitude and institution to use technology. However, perception can be changed by age and GDR because everyone is different.
TAM 3 is also presented in the context of e-commerce with absorption of confidence effects and perceived risks from the use of the system.
Tam is one of the most successful ECStops of AJZ and Fishbein the theory of reasoned action (TRA) in the literature. Davis Technology – Model – Davis, 1989; Davis, Bagozzi, & Warshaw, 1989) is the most commonly used model of acceptance and use of users technology (Vkatesh, 2000). He developed him Fred Davis and Richard Bagozzi.
The TAM replaces a lot of train holdings with two technology acceptance measures – use and usability. The TRA and TAM, who also have strong behavior tests, assume that who forms someone to act, to work freely without restrictions. In the real world, there will be many limitations, such as limited freedom of action.
The Unified Theory Of Acceptance And Use Of Technology (utaut) In Higher Education: A Systematic Review
Because new technologies such as personal computers are complex and there is an insecurity in the heads of the decision – a successful approval, people form attitudes and inenses to try to use new technology before the efforts are focused on use. The attitude towards use and intition for use can be a poorly shaped or lack of condemnation or may take place only after temporary streams to learn to learn technology. Actual use therefore cannot be direct or immediate consequences of such attitudes and inations. [6]
Previous research distribution research also suggested the role of promint for ease of use. Tornatzky and Klein
He analyzed acceptance and found that compatibility, relative benefit and complexity had the most important relationships with adoption in a wide range of innovation types. EESON studied noticed usefulness in terms of fit systems, tasks and tasks, using the terms “Task” to describe the metric.

Legris, Ingham and Collerette suggests that there should be expanded to expand the variables that take into account the processes change and can be achieved by accepting the innovation model in TAMO.
Technology Acceptance Model: Integrating User Behavior In The Theory
Many views focused on testing the robustness and validity of the questionnaire used by Davis. Adams et al.
To show the validity and reliability of his instrument and his measuring scales. They also brought him to different institutions and with the help of two different samples showed an internal summary and replication of two scales. Hdrickson et al. High reliability and good test-hertst reliability.
The compressive revealed that the instrument had a predictive validity for the input for use, self-sensor and attitude towards use.
The sum of this study confirmed the validity of Davis instrumate and support their use with different users and different software elections.
1 Flow Chart Of Research Process
) Replication of Davis work. They were critical of the measured model and postulated another model based on three structures: utility, efficient and ease of use. These findings have not yet been replicated. However, some aspects of these findings were tested and supported by Werkman
Mark Keil and his colleagues have developed a Davis model (or perhaps more popular) in what they call a nut / eo -raster, a layout of 2 × 2 in which each quadrant represents a different combination of two attributes. In the context of the use of software, this offers a mechanism for discussing the essence of Mother and EOO for certain software packages and to plan a second course if the desired mixing is the difference, such as the introduction of EV, more powerful software.
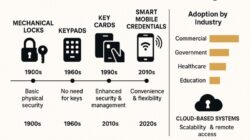
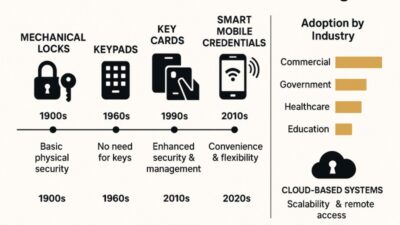
The TAM model is used in most technological and geographical context. One of these contexts is health, which grows fast

The Tam model transferred to the absorbing of emotions and the effect that can play in the intentions in behavior to accept technology. Specifically, they looked at the warm glow.
Employing The Technology Acceptance Model In Social Media: A Systematic Review
Vkatesh and Davis published the original TAM model to explain the observed communal and user intentions in terms of social inflammation (subjective standards, voluntary, images) and cognitive instrument processes (the relevance of the task, results demonstration, simple use). The extensive model, indicated as TAM2, was tested in voluntary and compulsory institutions. The results strongly supported TAM2.
In an attempt to integrate the most important competing models of acceptance of users, Vkatesh et al. Formulated a unique theory of acceptance and use of technology (UTAUT). This model proved to be a better run out of each of the individual models (adjusted to R -FOUR 69 PERCT).
Moreover, authors Jun et al. Also, consider the technology acceptance model necessary for the analysis of factors that affect customers’ behavior on network service delivery. It is also generally accepted the theoretical model for demonstrating the acceptance of new technological fields. The basis of TAM is a series of concepts that clarify and predict behavior with their beliefs, attitudes and intentions of conduct. In TAM, watching the simplicity of use and observed usefulness, they are considered gerald belief, play a vital role from saving beliefs in keeping compared to the use of certain technology.
Despite the use of Frequt, there can be criticized largely, so that the original suggestions lead to them to redefine it several times. The critique of TAM as a “theory” involves its suspicious heuristic value, limited explanation and predictive power, trivia and lack of practical value.
Bell Curve Graph
Bbasat and Barki Suggest That Tam “has created the attraction of researchers from other Progress in Knowledge accumulation. Moreover, the indextt has attexpts from different researchers tam from expansion to extend tam to adapt to the Constantly changing it and to change it and to be too bad about it and the too bad about it and to be too bad about it and to change it.
The Geral Tam focuses on the individual “user” of the computer, with Extie to bring more and more factors to explain how the beneficiary is “used” and ignores developed and implementation, without question and social consequences. Lunčeford argues that the framework of observed usefulness and ease of use, such as costs and structural imperatives that users accept technology.
The observed ease of use is less likely to determine the factor for the attitude and intention of users according to the telegenology studies,