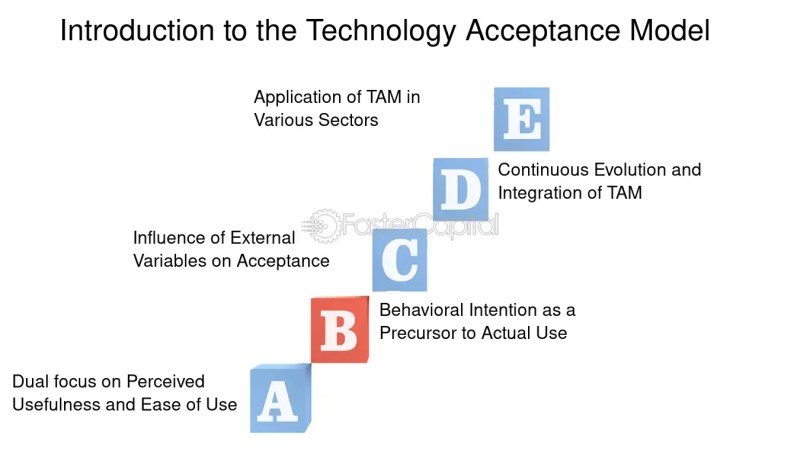
Technology Acceptance Model Tam Theory – An example of technological acceptance (TAM) is a theory of information systems that shows how users accept and use technology.
The use of a real system is point D where people use technology. Entry behavior is something that causes people to use technology. Internal character (Mrs) has power and perspective (a) which is the printing of geeral technology.
Technology Acceptance Model Tam Theory

An example shows that WHH users have new technologies, a number of factors affect their decision on how and that they will use it, which is:
Proposing Value-based Technology Acceptance Model: Testing On Paid Mobile Media Service
External standards such as social influence are an important factor in determining perception. What these (TAM) are in place, people will have a view and within using technology. However, the perspective can change age cleansing and cleansing because they are all different.
TAM 3 was also recommended in the context of E -commerce and the incorporation of the nerve and risk effects identified in system use.
It is also one of the worst exceptions of AJZ and Fishbein theory on the point of thinking (TRA) in literature. An example of the acceptance of Davis technology (Davis, 1989; Davis, Bagozzi and Warshaw, 1989) is the most commonly used model for consumer use (Vkatesh, 2000). It was organized by Fred Davis and Richard Bagozzi.
It also replaces multiple steps of tras view with two technological acceptance steps: ease of use and use. TRA and also, who all have behavioral matters, think that anyone creating a step, which will be free to act without hindrance. In the real world there will be many barriers, such as the limited freedom to act.
Technology Acceptance Model Word Cloud Composition Stock Vector (royalty Free) 2305503925
Because new technologies such as personal computers are complicated and there is an elemt of uncertainty in decision -making -minded -mindedness of their adoption, people create attitudes and try to learn to use new technologies before starting efforts to use it. Attitudes towards use and use of use can create a negative or lack of guarantees or may occur only after the first hit to learn how to use technology to break. As such, true use may not be a direct or immediate result of perspectives and experiments like this. [6]
Old research on the distribution of invention has also suggested a popular role for the ease of recognized use. Tornatzky and Klein
He analyzed the adoption, discovering that compatibility, relative benefits and difficulty had the most important relationship and the adoption of a variety of innovations. Eason has read the recognized uses in terms of modified systems, functions and profiles, using the words “functional correction” to describe metric.

Legris, Ingham and Coletette recommend that they must be forced to include parameters that cause change processes and that this can be achieved by adopting an example of innovation in TAM.
Unified Theory Of Acceptance And Use Of Technology [personality & Tkms Series]
Many modifications were intended to test the power and validity of the teaching questionnaire used by Davis. Adams et al.
Showing the validity and reliability of your teaching and measurement scales. They also expanded it to a different configuration and, using two separate samples, showed the internal position and reliability of the replication of the two scales. Hdrickson et al. Get high reliability and reliability of a good test.
Szajna found that teaching was predicted for the use of personal and personal use and attitude towards use.
The sum of this study confirmed the validity of Davis’s teaching and supported its use with different numbers of users and different software options.
Technology Acceptance Model (tam) –
) Replication of the work Davis. They criticized the measurement model used and set a separate model based on three construction: use, efficiency and ease of use. These results still do not appear to be changed. However, several aspects of these findings have been tested and supported by an employee
Mark Keil and his colleagues developed (or, perhaps the most popular) the example of Davis in what they call the usage/eou network, which is a 2 × 2 network where each quadrant rejects the different combinations of the two features. In the context of software use, this provides a mechanism for discussing the use and combination of Eou for certain software packages and drawing different courses if different combinations are required, such as introduction to the most powerful EV software.
The Tamo model was used in the technological and geographical context. One of these contexts is the health care, which grows fast

It added the TAM model to incorporate the emotions and the effect you can play in the character to accept the technology. In particular, they looked at the brightness of the heat.
The Applicability Of The Modified Technology Acceptance Model (tam) On
Vkatesh and Davis added TAM’s original model to explain the importance and use of use in terms of social influence (subjective, voluntary rules, images) and cognitive tool processes (functional importance, output quality, results of results, ease of recognized use). The separated model, called TAM2, has been tested in voluntary and mandatory configuration. The results were very helpful in TAM2.
In an attempt to integrate the main models of acceptance of competitors, vkatesh et al. He developed a unified theory of acceptance and use of technology (TAUT). This model has been found, which exceeds each of the individual models (69 -square).
In addition, the authors Jun et al. He also thinks that a model for technological acceptance is important to analyze the factors that affect customer behavior towards food delivery services. It is also a great example of the theory that is widely applied to the acceptance of the new fields of technology. The basis of TAM is a layer of concepts that define and provide human behavior and their beliefs, attitudes and inner behavior. In TAM, the ease of use and use recognized, focused on the beliefs of Gerares, plays a more important role than the beliefs imposed by salt in the views towards the use of certain technologies.
Tam was widely criticized, despite its use of Frequt, causing natural suggestions to try to re -elaborate it several times. TAM criticism as “theory” includes its question of interrogation, expressive power and minimal prediction, difficulty and lack of practical value.
An Extension Of Trust And Tam Model With Tpb In The…
Bbasat and Barki propose that they have “directed the balance of researchers away from other important research issues and to create developmental illusion in the collection of knowledge. In addition, independent experiments of several researchers extend the size to change it and change the constant change.
In Geral, it also focuses on the “user” of the computer’s individual, and the idea of “recognized use”, and eets to bring more and more things to explain how the user “discovers” “importance” and ignores social social processes is use and implementation, of course where the most technological is the best, and the social outcome of it is use. Lunceford argues that the system of consumption and ease of use ignores other problems, such as the cost and structural importance that forces users to adopt technology.
The ease of recognized use is unlikely to be the layout of the view and the use of a telemedicine study, an example of technology acceptance (TAM) is a theoretical system designed to explain how users adopt and use technology. It is a widely used example that has been used in various fields, as well as information, marketing and social science systems. TAM was proposed by Fred Davis for the first time in 1986 and has since been revised and expanded by several researchers.

TAM is equipped with two basic devices: identified use (PU) and ease of identified use (Peou). PU refers to the extent to which the user believes technology will improve their performance or productivity. Peou refers to the rate that the user believes technology is easy to use. According to TAM, these two factors are the main indicators of consumer acceptance and use behavior.
Applying The Technology Acceptance Model (tam) In Information Technology System To Evaluate The Adoption Of Decision Support System
Although Pu and Peou are the main factor in TAM, external factors can also influence consumers’ acceptance and use behavior. These factors include social standards, organizational factors and individual differences. Social rules refer to the expectations and beliefs of others on the user’s social network. The reasons for the organization refer to the Consumer Procedure, Procedures and Culture. Personal differences refer to factors such as age, gender and experience.
TAM has been widely used in several fields to read users’ adoption and use behavior. Used in the context of e -commerce, mobile technology, social networks
And health technology, among others. TAM was also used to promote and evaluate measures aimed at increasing the adoption of consumer use behavior.
Despite its widespread use, TAM was criticized for its limited scope and prediction. Some researchers have argued that TAM does not focus on factors such as social influence, confidence and risk. Some have said that TAM does not provide the harsh behavior of consumers.
Application Of Theory Of Technology Acceptance Model (tam) In The Hospital
In order to address some TAM criticism, several researchers have proposed extensions and modifications for example. For example, a unified theory of acceptance and use of technology (TAUT) includes additional factors such as performance expectations, efforts for effort, social influence and enabling conditions. Some researchers have recommended TAM modifications to account for context or special users groups.
Acceptance of technology
Educational technology theory, acceptance theory, technology acceptance model davis 1989, tam technology, disruptive technology theory, tam technology acceptance model, big bang theory tam, technology acceptance model tam questionnaire, technology acceptance theory, technology transfer theory, technology acceptance model theory, acceptance commitment theory