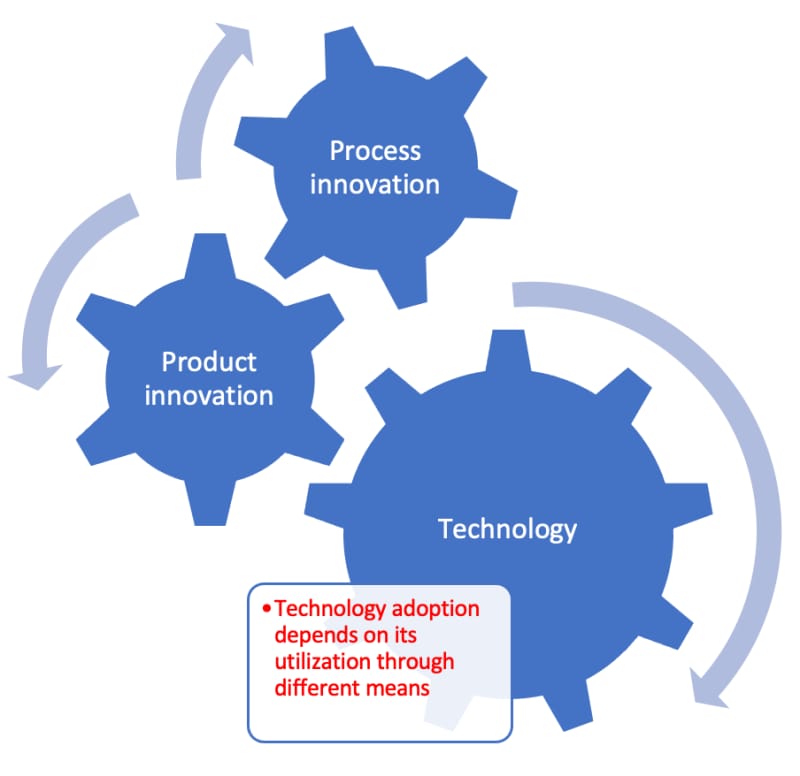
Technology Adoption Picture – Acceptance of changes based on normal distribution with five groups divided by attitude toward adoption of change and depth.
Agile Image Infographic Leadership Photo Photo Postter Development of Technology Technology Technology Adoption of technical living adoption
Technology Adoption Picture

The model describing the acceptance of innovations. On the basis of normal distribution, there are five groups of adopters divided on the basis of the attitude of adoption of change. The model also describes the depths that represent the step from the first users to the majority.
Technology Adoption By The Accountancy Profession Survey 2022
Through technology as the purpose of their committed changes, they are pursuing new technologies. Usually before it is public. There is not much and they are not willing to pay a lot for a product. However, they allow you to test the product in real environment. Innovators are more risky -oriented and invest in product review.
Compared to those who change, the goal of the first users is to buy a new technology to create their own vision. Purchase risks are not very sensitive to price. These are leaders of opinion that can inform the rest of the new technology market. It uses the judges of new technology.
The pragmatic most is more acute of change and based on the opinion of the first to adopt. Technological success is based on the transition from the first users to the early most. They have a strong sense of practicality, so they want to see the combined references before investment.
Conservatives or late are mostly traditionalists waiting for technology to be an integrated -with -the standard. They usually do not want to make changes to the average part of the market and therefore adopt technology due to pressure on them.
Conquering The Product Adoption Curve: A Comprehensive Guide
Believers believe that technology rarely maintains promises made. They are seen as resistors to change, but they may have other factors that are not modern as a lack of resources or knowledge. On the other hand, as they have many topics against change, they can help improve the change itself.
Framework CIDI CIDI framework is a systematic approach for creating artificial intelligence instructions consisting of four main elements: context (background setting), instructions (provides clear directions), details ( specific specifications of parameters) and input (which provides the materials required). This organized procedure guarantees complete communication with artificial intelligence by guiding users by logically providing all important information, from establishing the situation to … Softly outline . The paper (paper (paper (paper (paper (paper (duty, context (giving background) and performance (clear settings for delivery). Doing essential and urgent tasks in this dial requires immediate attention and important for your goals Producers rely on uninterrupted blocks of time to deal with complex and creative problems that require a deep focus and prolonged attention. Deciding and effectively cooperating with teams. It should describe why it is important. In this way it contributes to the creation of identity. Flowing the flow of values, the flow of the flow values is a slender procedure for flowing the flow and improving the processes that provide to monitor the flow through a process. Minto Pyramid The principle of Minto Pyramid, a communication framework, supports a top-down approach to send messages effective Spotify Health Check Spotify Health Control is a seminar, in which teams review their project and cooperation using 11 dimensions. The maslow hierarchy of the needs of the hierarchy of the needs of the needs relates to the basic needs and preferences of the person, underline that safety needs should be satisfied before the increased need. The Matrix Rachi Matrix/Raci Graphic is the type of Matrix of Assignment for an effective work organization, communication responsibilities. 1962, sociologist Everett Rogers published the book “Spread of Innovations” in which he ranks with consumers in unique groups with various purchase habits that summarize research from more than 500 these studying the dispersion. Today, the model is better known as the technological life cycle and describes the adoption or acceptance of a new product or change (technological), according to the demographic and psychological properties of 5 unique groups of adopt. In this article, we will explain the model and review 5 groups of adopters in the way. In addition, we will look at Geoffrey Moore’s marketing techniques to cross the depths to successfully hit the mainstream of consumers.
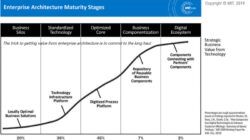
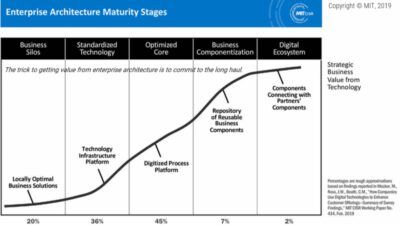
As can be seen in Figure 1, the technology -adoption cycle cycle has a bell curve and the divisions on the curve are approximately equal to which the common deviation has fallen. This means that innovators represent about 2.5% of the total population, the first to adopt about 13.5%, the early most and the latter most of the same 34% and lateComers remaining 16%. Each group represents a unique psychographic profile (i.e. a combination of psychological and demographic characteristics) that makes marketing responses other than other groups. By understanding the differences of these groups, Marketeers better direct all consumers with the right marketing procedure.

Innovators are the first group of people who are probably invested in your product, as they pursue new technological aggressive products. Sometimes they even look for them even before launching a formal marketing program. This is because technology is a major interest in their lives, no matter what it plays. The disadvantages are that there are not many changes (about 2.5%) in a specific market segment and are usually not willing to pay much for new products. However, covering them is still important, as their approval assures other market buyers that the product may work. In addition, these technology lovers can serve properly as a test group to make the necessary changes before targeting the mainstream.
Technology Adoption: Key To Business Success
The first users, such as innovators, get a new product concept in advance of its life cycle. However, unlike those who change, they are not technologists. Instead, they are visionaries that not only seek an improvement, but for a revolutionary point of construction. As a result, they are willing to run a great risk of testing something new, they are the least sensitive to the prices of adoptants and very demanding. The first users had a lot of (about 13.5%) and not based on the combined -with the references to making purchase decisions. Instead, they prefer to rely on their intuition and vision. In addition, they are willing to serve as highly visible references to other population adoption groups. Because visionaries are well informed of the rest of the population, they are the most important importance to conquer.
‘Beginning with the initial majority. These pragmatists share some of the first skills of the first adopted technology, but eventually they are guided by a strong sense of practicality. They know that many inventions end up going from fashions, so they enjoy waiting and see how other people get to know before buying themselves. They want to see the combined -with -the -way references before investing significantly. Because there are so many people in this segment (about 34%), conquest of these people is important for any company dedicated to huge income and growth.
The latter most as a group is as large as the early majority (34% of the total population). They share all the concerns of the initial majority including one more important: they believe more in tradition than developing. While people in the early most are comfortable with their ability to manage a new technological product, if they finally decide to buy it, members of the late majority will not. As a result, these conservatives prefer to wait for something to be a combined -with -the standard and invest only at the end of a psychological cycle of life. And even if they want to see a lot of support and tend to buy only from large and combined -with -companions. Being a market leader is therefore an important requirement to win the late majority.
Finally there are remaining 16% of the population: the lateComers. These people don’t want anything to do with new technologies. The only time they do not buy a technological product is when it is buried deeply with another product. These skeptics strongly believe that disturbing changes rarely keep their promises and almost always cause accidental consequences. From the point of view of market development,