Technology Of Acceptance Model – This is part 7 of the series of articles with edited parts of the dissertation of Dr. Morin Sullivan.
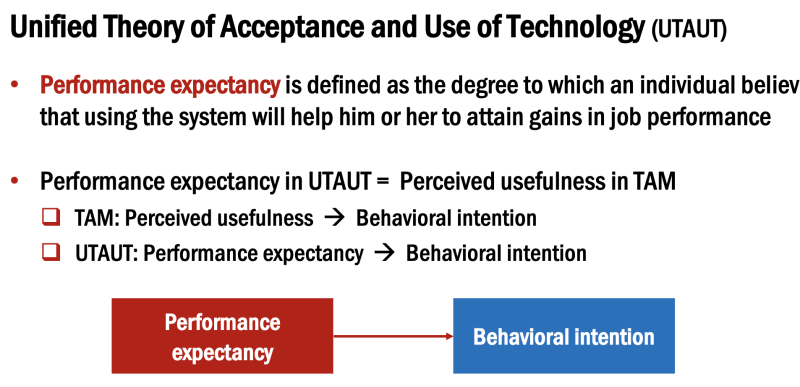
Wenkatesh and Davis developed the expansion of the technology adoption model (TAM), in which they outlined the perceived usefulness and intentions of use associated with the processes of social influence and cognitive instrumental
Technology Of Acceptance Model

Wenkatesh and Davis reported that the perceived usefulness is based on the intentions of use in many empirical TAMs. It is important to understand determinants of the perceived design of usefulness, since it stimulates the intentions of use and how these determinants affect changes over time with an increase in the use of the system. Although the original TAM model was based on the determinants of the perceived ease of use
How To Predict People’s Intention To Use A New Technology?
The determinants of the perceived usefulness allowed organizations to develop organizational interventions that will increase the adoption of users and the use of new systems. For this reason, Venkatesh and Davis conducted a study published in 2000 to expand TAM, which studied how the perceived designs of utility and intentions using a permanent information system (IS) were changed.
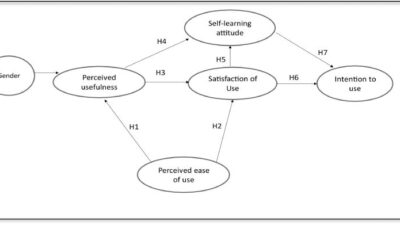
Figure 1 shows a graphic overview of the proposed model of the Hungarian and Davis, called TAM2. The TAM2 model added: “Theoretical constructions, including the processes of social influence (subjective norm, voluntariness and image) and cognitive instrumental processes (relevance of work, the quality of the output, demonstration of results and the perceived ease of use).”
TAM2 includes a subjective norm, voluntariness and image, which are three interconnected social forms. These forms help determine whether a person will accept or reject a new system. In addition to these three forms, Venkatesh and Davis indicated that cognitive determinants of the perceived usefulness in TAM2 can be described as the perceived ease of use, development, quality of release and relevance of work. These instrumental determinants are defined in Figure 2.
In accordance with the theory of reasoned action (TRA), the subjective norm is that other people important to the subject think about an object that performs or does not perform certain behavior. TAM2 indicates that “in the context of using the computer, the direct effect of the subjective norm based on direct correspondence to the intention up and above the perceived use (PU), and the perceived ease of use (PEOU) will occur in the mandatory but voluntary settings for the use of the system.” In TAM2, voluntariness, therefore, is displayed in the form of a modifying variable. TAM2 assumes that the subjective norm has a positive effect on the image, because if the working group of a person considers it important to perform the task (for example, using the system), the performance of the task increases the image of a person in the group. In addition, “TAM2 theorists that the direct influence of the subjective norm on intentions for mandatory contexts of use will be strong before implementation and during early use, but over time it will weaken, since an increase in direct experience with the system provides a growing basis for intentions for constant use”.
Extending The Technology Acceptance Model To Explore Students’ Intention To Use An Online Education Platform At A University In China
The relevance of work, the quality of the output, the demonstrativeness of the results and the perceived ease of use are a series of determinants of the perceived usefulness in the TAM2 model. The relevance of the work is based on the ability of the system to support the function of human work. Wenkatesh and Davis described “the quality of the exit as a perception of the individual about how well the system performs a certain task.” The result of the demonstration implies that people will have a more positive attitude to the usefulness of the system, if the differences between use and positive results can be easily observed. In addition, the perceived ease of use is studying how easy or easy to use the system. Wenkatesh and Davis claimed that TAM2 suggests that all cognitive instrumental processes positively affect the perceived usefulness and, ultimately, the intention of a person to use the information system.
In general, after the adoption of the system goes beyond the scope of an individual decision to solve the team, the processes of social influence should expand outside TAM2.
Dr. Mororin Sullivan is an official on information technology in the working space of the US Federal Government. She also teaches technological courses at the Maryland Public College. Dr. Sullivan continues his research in the field of technical knowledge management systems.

We use cookie files on our web -site to give you the most relevant experience, remembering your preferences and repeated visits. By clicking “accept”, you agree using all cookies.
Teori Lengkap Tentang Technology Acceptance Model (tam) Menurut Para Ahli Dan Contoh Tesis Technology Acceptance Model (tam)
This website uses cookies to improve your experience while moving on a website. Of these, cookies, which are classified as necessary, are stored in your browser, since they are important for the main functionality of the website. We also use third -party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this site. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. You also have the opportunity to abandon these cookies. But the abandonment of some of these Cookie files may affect your viewing experience.
The necessary cookies are absolutely necessary for the correct functioning of the website. These cookies provide the basic functionality and safety functions of the website, anonymously.
This cookie file installed under the consent of the consent of the Cookie GDPR is used to record the consent of the user for cookies in the “Advertising” category.
This cookie file is installed by the cookie cookie gdpr plugin. Cookie is used to store user consent for cookies in the Analytics category.
Fisheries And Aquatic Sciences
Cookie is established by the consent of the cookie GDPR to record the user consent for cookies in the category “Functional”.
This cookie file is installed by the cookie cookie gdpr plugin. Cookies are used to store the user consent for cookies in the category of “necessary”.
This cookie file is installed by the cookie cookie gdpr plugin. Cookie is used to store user consent for cookies in the category. “

This cookie file is installed by the cookie cookie gdpr plugin. Cookie is used to store user consent for cookies in the category “performance”.
E-learning The Role Model Technology
Cookie is installed by the cookie cookie gdpr plugin and is used for storage whether the user agreed using Cookie files. He does not store any personal data.
COOKIE productive files are used to understand and analyze the key productivity indexes of the website that help provide better user work for visitors.
This cookie file is installed by Google Universal Analytics to limit the speed speed and thus limit the data collection on sites with high traffic.
Cooking analytical files are used to understand how visitors interact with the web site. These cookies help to provide information about the indicators of the number of visitors, the refusal indicator, the traffic source, etc.
The Mobile Payment Acceptance Model Of Chinese Residents
Cookie _GA installed by Google Analytics calculates data on visitors, session and campaign, and also monitors the use of the site to report on the site analytics. Cookie stores the information anonymously and prescribes an accidentally generated number for recognizing unique visitors.
Installed Google Analytics, _gid cookie stores information on how visitors use a website, and also create an analytical report on the productivity of a website. Some of the collected data include the number of visitors, their source and pages that they visit anonymously. The technology adoption model is the theory of information systems that model how users accept and use technology.
The actual use of the system is a DOCK where people use this technology. The behavioral setting is a factor that makes people use this technology. Behavioral guidance (BI) is filled with an attitude (A), which is a herard impression of technology.

The model assumes that WH users claim to be new technology, a number of factors are conceiving their decision on how WH, in particular, they will use it:
Top 10 Technology Acceptance Model Powerpoint Presentation Templates In 2025
External variables, such as social radiation, are an important factor for determining the relationship. In -this is on the spot, people will be related and imposed for the use of this technology. Nevertheless, perception can change the department for age and GDER, because all are different.
TAM 3 was also proposed in the context of e -commerce with the inclusion of the influence of trust and perceived risk on the use of the system.
TAM is one of the most delightful AJZ urns and the theory of the reasoned action of Fishbein (TRA) in the literature. The Davis technology adoption model (1989; Davis, Bagozzi, & Warshaw, 1989) is the most widely applied model of the adoption and use of user technologies (VKATESH, 2000). It was developed by Fred Davis and Richard Bagozzi.
TAM replaces many of the TRA measures in relation to the TRA attitude with two measures of technology – branching and usefulness. TRA and TAM, both of which have strong behavioral elements, suggest that someone forms the imposition to act, that they can act freely without restrictions. In the real world, there will be many restrictions, such as limited freedom to act.
On Technology Acceptance Models
Since new technologies, such as personal computers, are complex, and in the minds of persons who make decisions, there is an exception to the successful adoption of them, people form an attitude and skills to try to use new technologies before the start of efforts aimed at use. The attitude to use and instructions on use can be poorly formed or not condemn, otherwise it can only occur after preliminary desires to learn how to use development technology. Thus, the actual use cannot be a direct or direct consequence of such attitudes and overlays. [6]
Early studies about the spread of innovation have also offered the first place for the perceived simplicity of use. Tornatsky and Klein
I analyzed the adoption, discovery that compatibility, relative advantage and complexity had the most significant relations with the adoption of innovative types in a wide range. Ison studied the perceived usefulness in terms