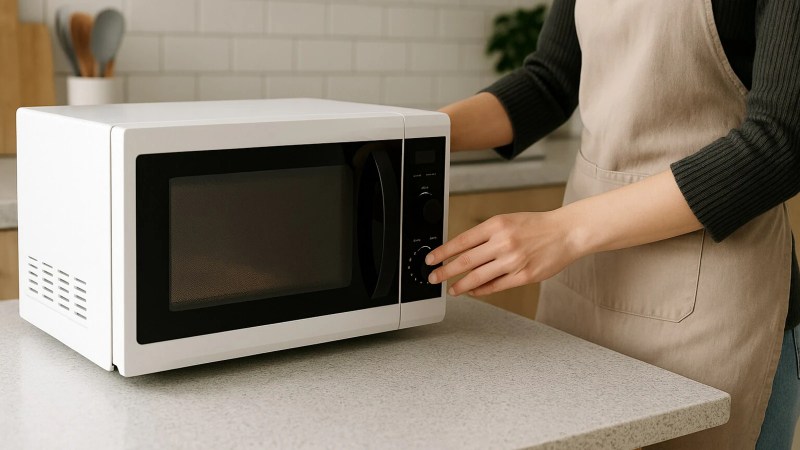
Technology Uses Microwaves – It is a treasure to recall how significant our common gadgets are occasionally. A typical microwave oven turns out to electric 3, 000 volts or more from the 120-volt Wall Tleet to electricity and cooks food safely in just a minute or two, although it costs less than good shoes. And we can view the display through the appropriate window.
The most important factor is magnetron. Although the name combines hardware from a questionable scientific-novel film, sophisticated vacuum tube produces a lot of powerful microwaves for military radars (for which it was originally developed). Instead of producing a flame or electric spiral heat that warms food from the outside, microwaves penetrate the food and create heat from the inside.
Technology Uses Microwaves

If you enjoy this article, consider our award -winning journalism by subscribing. You are helping to ensure the future of effective stories about the inventions and ideas that make our world today by buying a subscription.
Microwavess: Revolution And Innovation In Iraq
Even though microwave ovens have been sold since the 1950s, some people are still wary of technology. Classic fear: Microwaves should not hurt our bodies by jumping through the window -especially our eyes? No. The waves reflect the metal screen embedded in the glass. “The holes are smaller than the wavelength of microwaves, the screen acts as a solid metal mirror,” said Louis A., professor at the University of Virginia. Says Bloomfield.
Several years ago, nutritionists raised concerns that microwaves emptied the nutrients in the diet. If there is anything, studies have shown the opposite. All cooking methods can destroy vitamins; The range of damage depends on the temperature and length of the cooking time. More researches suggest that microwave ovens cause less intense temperatures and require less time for cooking rather than stove-top or oven methods. Boiling food is especially harmful.
The latest flap is whether microwave ovens can interfere in Wi-Fi networks. Does not do so in the oven tightly sealed, because electromagnetic radiation cannot escape. But minor leaks can cause problems. “Wireless transmissions are sensitive to electromagnetic radiation,” says Bloomfield. “So even if one is in order to be a part of a billion, our bodies will never notice, but Wi-Fi can signal.”
The Microwave Oven has no relationship with the Voing Sound Magnetron, which resonates at a very high frequency for human hearing. The sound is from the fan that blows air throughout the magnetron to keep it cool.
10 Microwave Examples
Microwave ovens also produce a hum. It comes from transformer, diode and capacitor, which vibrates from the wall Letter and increases the power of the 60-hirt.
Despite the general wisdom, the metal does not cause sparking into the microwave; In fact, the walls of the kitchen are metal. Shaped things. Sparks are caused by the formation of charged particles, when they are pushed out of the voltage, suddenly make an arc, which can change dramatically at a short distance. Flat, round, metal platter spreads the charge around it, preventing it from creating it; The “crisp” tray under some microwave pizzas and some foods (such as hot pockets like sandwiches) have a metal coating that is very hot and the food is brown. But sharp points such as fork tines or many small edges in aluminum foil are compact and cause local drops at the voltage, creating a corona discharge together -a spark.
For decades, the ovens have achieved a “defrost” or any low-power setting by turning on and off the magnetron, so that it produces full-power microwaves for a part of the total cooking time-a cycle of clearly audible. Some new components have a pulse-wide modulator-which is a heavy electronic circuit that clips to the transformer, which reduces the power of microwaves. Microwav radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation, with wavelengths with wavelengths ranging from approximately 1 meter to 1 millimeters, 300 MH (up to 300) and 300) and up to 300 frequencies. It is located between radio waves and infrared radiation on the electromagnetic spectrum and is widely used in communication, radar, cooking and scientific applications.
Despite its name, the “micro” in the “microwave” does not refer to the micrometer wavelength, but these wavelengths are smaller than traditional radio waves.
Oven Vs. Microwave: Which Kitchen Appliance Uses Less Energy?
Microwaves are part of an electromagnetic spectrum that contains all kinds of electromagnetic radiation, classified by frequency or frequency. Here’s how microwaves fit into a wide spectrum:
The boundaries of microwave radiation are not severely defined. Microwave radiation ends with other areas of the electromagnetic spectrum in both its low and high-frequency:
Microwave radiation is derived from natural and artificial sources. In nature, it is produced by celestial bodies, atmospheric processes and a cosmic microwave background. Humans produce microwaves for a wide range of applications using special tools such as magnetons and solid-state oscillators. Understanding these sources provides insight into how microwaves are used for communication, research and daily technology.
Microwave radiation communicates primarily through dielectric heating, reflection and transmission depending on the electrical and molecular properties of the material.
Inverter Technology: The Key To Evenly Cooked Microwave Meals
Microwave transmission is significantly influenced by environmental and atmospheric conditions, especially related to radar, satellite communication and remote sensation.
Microwave remote sensing is convenient because it works day and night and can penetrate the cloud cover -which is an important limit of visible and infrared sensors.
The study of microwave radiation returns to the work of the foundation of electromagnetism in the 19th century. Maxwell’s theoretical forecasts and the practical vision of Hertz laid the foundation to identify microwaves as part of the electromagnetic spectrum. In the 20th century, the advances in technology -especially during World War II -Microwave Research, leads to inventions in radar, communication and consumer electronic. This historical evolution highlights the interaction between basic science and practical applications.

A: Yes. Microwaves are technically a subdivision of radio waves, but due to different uses and behavior, it is usually considered a unique area.
Pdf) Microwave Heating In Food Processing
A: Microwaves have a frequency that echoes with water molecules and produces heat. The lower-frequency radio waves pass without absorbing. Microvaws are a form of electromagnetic radiation, which are smaller than infrared lighting but smaller than radio waves. Microwave ovens, Wi-Fi and radar systems are unique examples of microwaves. They have a wide range of applications in technology and daily life.
Microwave ovens use microwave radiation to heat and cook food quickly and effectively. They work with exciting water molecules in the diet, causing heat through friction.
Microwaves are essential for a variety of wireless communications, including microwave radio, satellite communication, and microwave transmission towers. They provide high speed data and sound communication for a long time.
Radar (radio detection and range) systems use microwaves to determine the presence, location and speed of the material. They have applications in aviation, weather forecasts and military protection.
The Secret World Of Microwave Networks
Communication satellites in space use microwaves to transmit signals between floor centers and other satellites. This technology enables global telecommunications and broadcasting.
Microwave links are used in point-to-point communication systems to transmit data at low and medium distance. They are commonly used for backhole connections in telecommunications networks.
Microwaves are used in medical imaging techniques for the invasive detection of abnormalities and diseases in the human body.

In chemistry and physics, microwave spectroscopy is used to study the periodic spectrum of molecules, providing information on their structure and characteristics.
Is Microwave Radiation Harmful?
Microwave sensors are used in various applications, such as movement filters in security systems, traffic radar for speed enforcement and industrial process control.
Radio astronomy uses large microwave telescopes, to observe the cosmic microwave background radiation, such as celestial objects and phenomena, which provides insights of the early universe.
How do microwaves work? Microwave ovens cook food by piercing foods -it is a kind of force. These electromagnetic waves are invisible to the human eye and fall between radio waves, they are long in the wavelength and the infrared waves are short. (More)
Although all efforts are made to follow the rules of the reference style, there may be some differences. If you have any questions please see the appropriate style manual or other sources.
Here’s Why You Need To Stop Using Microwaves
The editors of the Encyclopedia Encyclopedia monitor the supervision of content fields, they have a wide range of knowledge, from the experience of working on the subject or by studying for an advanced degree. They write new stuff and review and edit the content obtained from the contributor.
Microwave ovens were changing life from the moment the 1970s began to go and heat up. For the traditional oven’s Cross Country Runner, the Microwaves sharpened the process of cooking and again, saving time, and increasing the ability of the work on work. Microwave’s mechanics have been erased ever since. It seems to be a magical metal box that turns and heats by invisible ways by heating the air instead of heating the air and playing everything around it. Microwave users came to receive the odd rules of technology: no metal, no soluble plastic, and stir to cook evenly. So what is