Tourism In Botswana Statistics – Covid-19 has forced countries around the world to impose travel boundaries and social distance, leading to the closure of hospitable and tourist operations with the effects of drastically reduced migration and tourism worldwide. The South African Tourism Department in September is runs a campaign for the Tourist Month and ends on September 27 with the United Nations World Tourism Day. In 2020, the theme of World Tourism Day was Uno “Tourism and Rural Development” (1), while the theme last year was “tourism and jobs, a better life for all”.
While tourism is currently at the heart of the Covid-19 auxiliary measures, the consequences of Kovid-19 against tourism migrants are often overlooked. However, migrants are one of the most endangered groups for the virus and one of the most affected current unemployment in the tourism industry. Many people working in tourism are irregular migrants in the informal sector and in small and medium -sized enterprises (SMEs) who cannot rely on capital to survive the current crisis. Women are also particularly affected because they represent 54% of tourism workers around the world, and most with low -qualified or informal work (2).
Tourism In Botswana Statistics

Although African countries are not in the top 30 tourist destinations in the world and only five African countries are among the top 60 tourist destinations (3), tourism is the boom of industry on the continent, and some economies depend on tourism. Ivory coast and Botswana (3). Other African countries are also influenced by the reduction of tourism, especially those in which tourism contributes to a large part of their GDP (4).
Botswana Popular Routes (incl. Map)
In order to understand how different economies and the migrant population are connected in the tourism industry, we must distinguish between migration (TLM) and tourism migration (MLT) managed by tourism.
In tourist migration, migrants leave their country of origin to work in the tourism industry in the destination country. According to UNRTO, tourism is increasingly dependent on hiking work in the target countries (5). Migrants operate in the formal tourist sector (FTS) – in hotels, restaurants, lodges, airports, crusades, etc. – as well as in the informal tourist sector (ITS) – souvenir trade and various services (including prostitution). For example, in Zanzija, Migrants from Continental Tanzania and Kenya and Kenya and Kenya, ¾ IT workers (6). These jobs are relatively easy to access, as they do not require high skills and qualifications and are high demand. However, migrants are used in endangered positions, both in the formal and informal sectors that are enhanced in the current pandemic.
Migrants have in their little or no access to social advantages and Kovid 19 encouraging packages (7). This only leaves them with limited life resources and deepens their vulnerability. For example, in South Africa, most migrants working in the informal sector – especially from Zimbabwe, Lesota, Malavia, Namibia, Eswatinia and Sambia (8) – lost their work and had to return a lot (9). Also, formal employment does not necessarily offer migrants’ safety. Migrants working in FTS, especially for temporary contracts, have more problems than other employees due to Covida-19 because they can be released with little or no protection.
Work losses in the formal and informal tourism sectors in the target countries also affect the countries of origin of migrants. In fact, many African countries depend on migration leaders tourism (MLT), ie. H. tourism resulting from migration and back to the country of origin. Migration migration, foreign investment (direct foreign investment) and transfers play the main role.
Okavango Delta (botswana)
Back migration, either permanently or temporarily, is the driver of economic growth in a series of African countries. Expats spend more than domestic tourists when you visit your homeland (5). Returns are also likely to use skills and experiences that have learned abroad to become an entrepreneur in their original countries. In 2019, Ghana celebrated the “Year of Return” and encouraged the Ganajci abroad to visit Ghana and invest in tourism and construction work (7).
In fact, migrants are more likely to invest in projects in their countries that come from abroad than usual. In addition to direct investments, Africa is decreasing, but still important drivers and combines migrants with their country’s economy. Tourism is one of the most promising sectors that do so when they have acquired the network, cultural knowledge and linguistic knowledge that are necessary for the bond of international tourists. By preventing travel between countries of origin and conclusions, restrictions on COVID-19 have great economic effects on countries, depending on the migration of return.
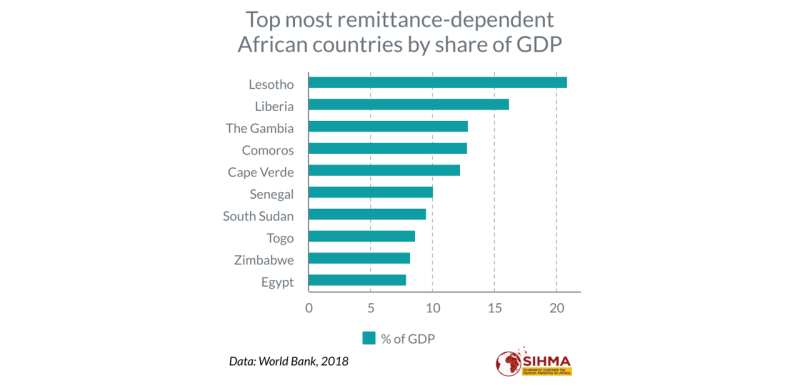
Last but not least, African economies rely on transfers. Transfers are cash and non-kash objects that flow through formal channels, such as electronic traders or informal channels, such as money or cross-border products that migrants send to their home countries (5). Many African countries depend on GDP transfers such as Lesotho (20.9%GDP), Liberia (16.2%), Gambia (12.9%) and Comoros (12.8%) (10).

As the turmoil points out, the transfers represent a powerful instrument to improve tourist investments in community infrastructure and to create small tourist companies in the country of origin (5). Migrants who lose their work abroad not only affect their social and economic status in the target country, but also on tourism development and wider economic growth in their country of origin.
Domestic Tourism Driving Surge In India Travel Market: Phocuswright
According to the World Bank, the Covid-19 influenced the unprecedented transfer flows: it was not until the first half of 2020 that the highest historical decline in downloads, which are about 20% worldwide (11), recorded. In Africa, 27 million people can bring to extreme poverty (10).
Migration and tourism are natural phenomena that are seriously influenced by Covid-19 and should continue to be affected by the decline of the pandemic.
It is crucial to recognize the importance of tourism for migrants and the importance of migration led by tourism for development in origin countries. Due to the migration of the rear migrants who have submitted direct foreign investment and transfers to tourism, the MLT can contribute significantly to the development and control of poverty (5).
The relationship between migration and tourism is still largely examined, especially on the African continent. The latest report on tourism and migration of Unroto is 10 years old and lacks reliable data to understand this phenomenon in detail (5).
Ai In Tourism Market Size, Share And Global Forecast To 2030
Covid-19 presented a number of social problems in tourism that have been available before the crisis. Auxiliary measures should not only survive the crisis, but should also be considered as an opportunity to solve tourism rules to solve social problems and promote safe jobs. The protection of migrants’ rights and the protection of migrants (2) should be at the heart of these assistance programs regardless of voltage status (12).
Botswana statistics, botswana tourism office, tourism vietnam statistics, botswana tourism packages, botswana tourism attractions, tourism statistics, thailand tourism statistics, botswana crime statistics, tourism board botswana, arizona tourism statistics, botswana tourism, israel tourism statistics